X線分光(超高速化学)
XFELを利用すると、高時間分解能(fs)・高空間分解能(sub-Å)・元素選択性を兼ね備えた時間分解X線計測が可能になります。これらの特性によって近年、超高速X線科学が急速に発展しています。SACLAでは、フェムト秒の時間分解能で時間分解X線吸収分光(TR-XAS)、時間分解X線発光分光(TR-XES)、時間分解X線溶液散乱(TR-XSS)を計測するための共用装置としてSPINETT(SACLA Pump-probe INstrumEnt for Tracking Transient dynamics)が利用可能です。本ページでは、SPINETTの構成や実験手順、代表的な成果について紹介します。
参考文献:
T. Katayama et al., Struct. Dyn. 6, 054302 (2019).
基本性能・成果
核波束振動の観測
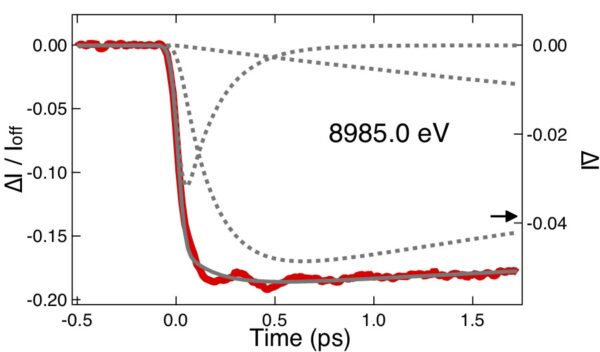 Cu(I)ビピリジン錯体の核波束
Cu(I)ビピリジン錯体の核波束
参考文献:
T. Katayama et al., Nat. Commun. 10, 3606 (2019).
化学結合形成の可視化
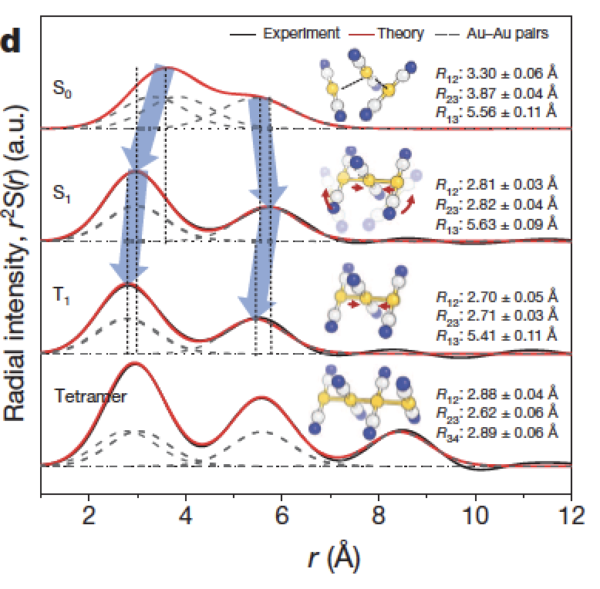 Au(CN)2錯体の結合の形成過程の追跡
Au(CN)2錯体の結合の形成過程の追跡
参考文献:
K. H. Kim et al., Nature 518, 385 (2015).
金属酸化物のキャリアダイナミクス
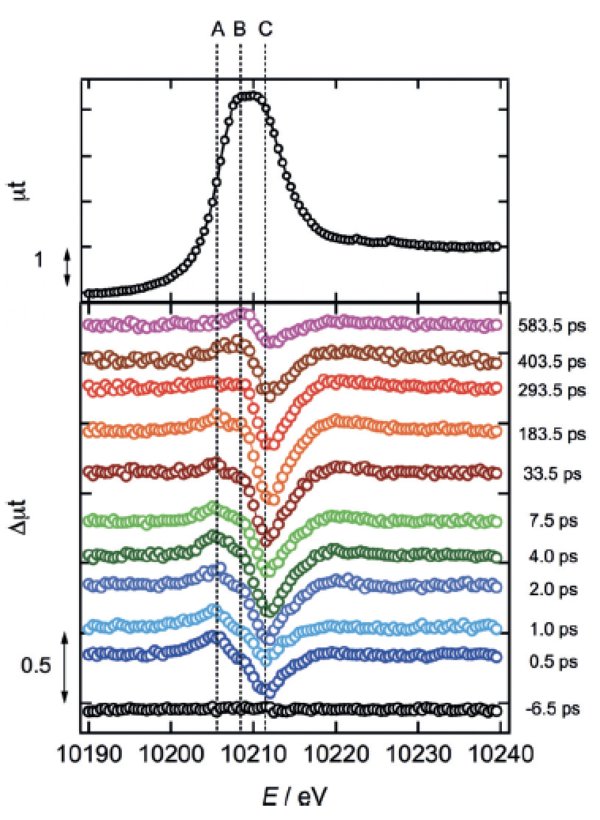
WO3 L-III edgeの時間分解X線吸収スペクトル
参考文献:
Y. Uemura et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 1364 (2016).
実験装置
SPINETTは試料チャンバー、Von Hamos型分光器、MPCCD検出器から構成されています。
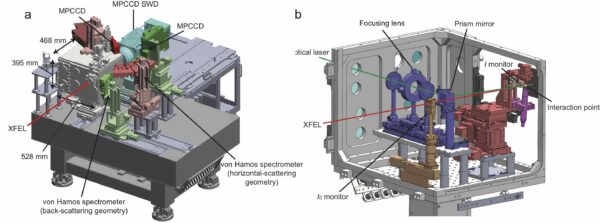
SPINETT概観
試料チャンバー
多くの場合、試料は溶媒に溶かし(分散させ)、溶液の状態でインジェクターからジェット状に吐出します。インジェクターの径は30~500 μmの間から選択することができます。(同期レーザーとXFELの媒質中の屈折率の違いから生じる群速度分散のミスマッチが計測の時間分解能に影響を与えるため、追跡したい物理現象に応じて選択します。)チャンバー内部には、2つのX線強度モニターが備わっており、TR-XASの実験の際には入射X線強度と試料からの蛍光X線強度を計測することができます。
Von Hamos型分光器
SPINETTは、TR-XESの実験のためエネルギー分散型の分光器を2つ備えています。分光器はそれぞれ、100mm×25mmの湾曲分光結晶(湾曲半径250mm)を6つ搭載可能です。現在利用可能な分光結晶として、Si(531)、Si(111)、Ge(111)、Ge(220)があります。独自の分光結晶を持ち込まれる場合、標準機器との干渉を避ける必要があるため、施設スタッフと十分な打ち合わせが必要です。事前にXFEL利用研究推進室(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)までお問い合わせください。
<p
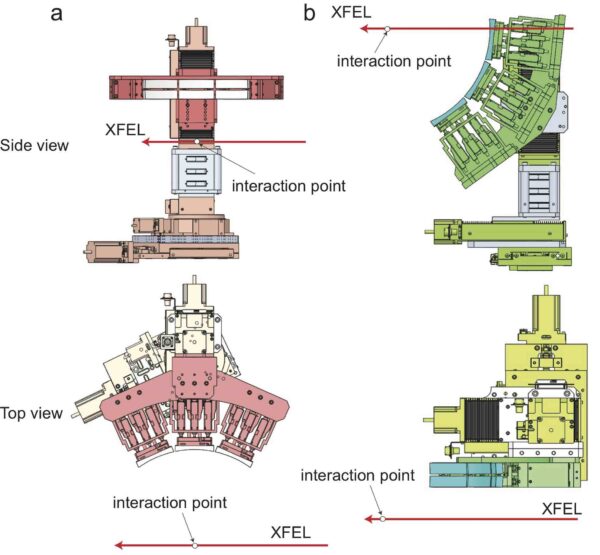
MPCCD検出器
von Hamos型分光器のため2つのSingle MPCCD検出器を、TR-XSSのため広角領域をカバーできるSWD Octal MPCCD検出器を試料チャンバーの外に配置しています。SWD Octal MPCCD検出器のカメラ長は、最短で~55 mmです。最短のカメラ長では、10keVで3.88Å-1、15keVで5.82Å-1の逆格子空間をカバーできます。
運転パラメータ(EH2@BL3)
時間分解X線分光の実験は主にBL3 EH2で実験を行なっています。
XFELパラメータ
| 光子エネルギー(基本波) | 4-20 keV |
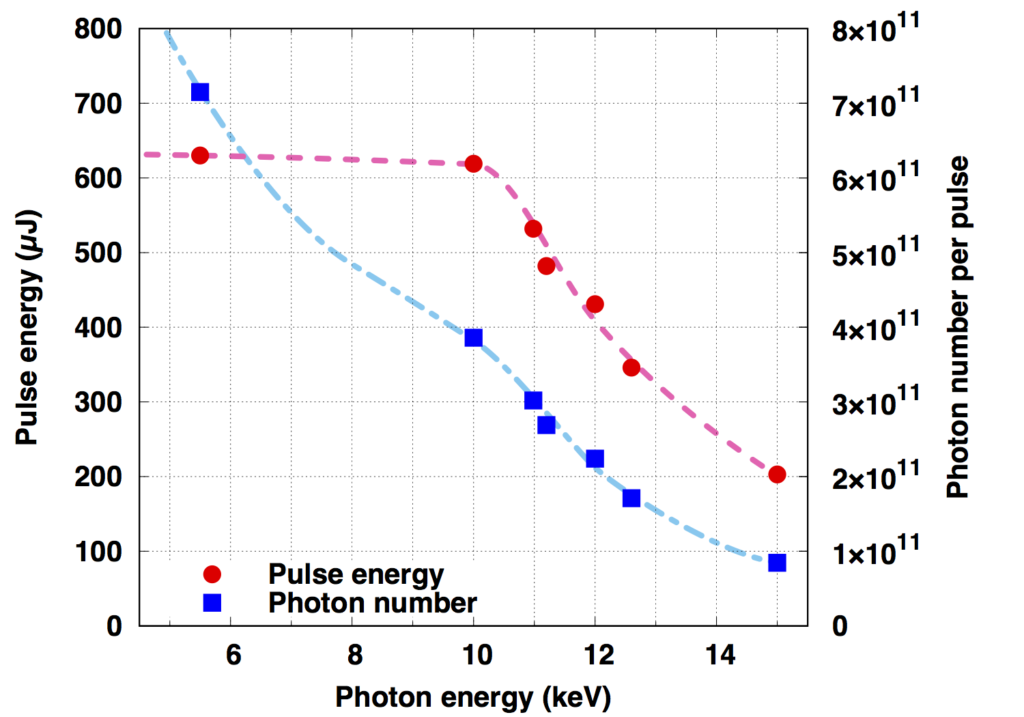
| パルスエネルギー | 光子エネルギーに依存(下図参照) |
| エネルギー幅(ΔE/E) | ~0.5%(ニ結晶分光器なし) |
| 繰り返しレート | 30 Hz(BL2&3同時運転時) |
参考文献:
M. Yabashi et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 22, 477 (2015).
K. Tono et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 595 (2019).
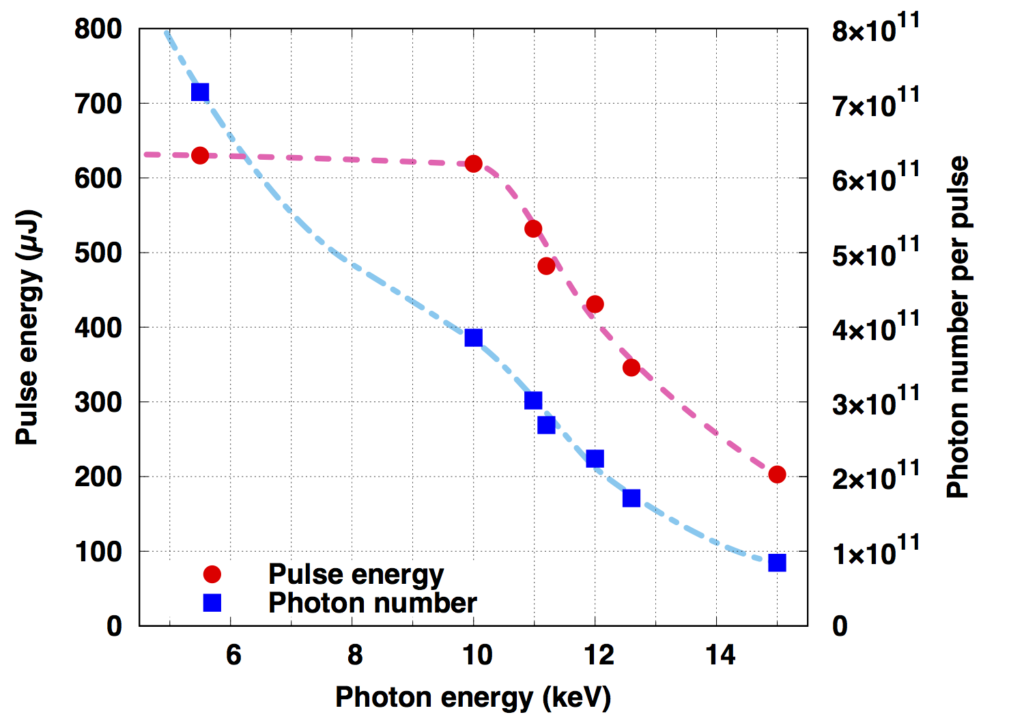
(参考)光子エネルギーとパルスエネルギー・光子数の関係(BL3の場合)
X線集光特性
| Optical parameters (CRLs) | |
| Material | Beryllium |
| Shape of lenses | Paraboloid |
| Radii of curvatures (R) | 200, 500 µm |
| Maximum number of lenses | 31 with R = 200 µm 15 with R = 500 µm |
| Focal length | 2.5 m |
| Spatial acceptance | > 0.9 mm |
| Divergent angle | > 0.1 mrad* |
| Typical focal size @10 keV | 1-2 µm FWHM* |
*使用するレンズの数や波長に依存します。
参考文献:
T. Katayama et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 333 (2019).
光学レーザー特性
| 基本波 | 2倍波 | 3倍波 | 4倍波 | |
| Wavelength | 800 nm | 400 nm | 267 nm | 200 nm |
| Pulse Energy (Max.) | ~12 mJ | ~0.5 mJ | ~0.2 mJ | ~0.02 mJ |
| Pulse Duration | ~40 fs | ~30 fs | ~50 fs | |
| Rep. Rate | 60 Hz | 60 Hz | 60 Hz | 60 Hz |
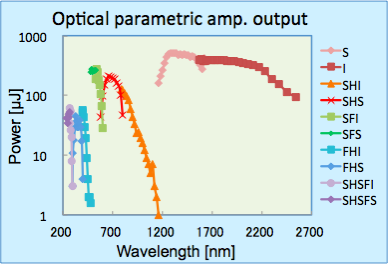
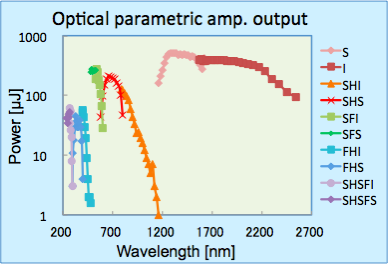
上記に加え、光パラメトリック増幅器(OPA: Optical Parametric Amplifier)からの光を利用可能です。使用可能な波長域は0.25-2.6 µmで、下図のようにパルスエネルギーは波長に依存します。
測定までの調整作業
ビームタイム前・ビームタイム中にスタッフが行うこと
- ・装置を実験ハッチに搬入
- ・XFELのスペクトル測定、光軸調整、集光調整
- ・モノクロメーターのアライメント
参考文献:
T. Katayama et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 333 (2019).
- ・von Hamos型分光器のアライメント
- ・4象限スリットのアライメント
- ・MPCCD検出器のアライメント
- ・同期レーザースペクトル、光軸、集光の調整
- ・XFELと同期レーザーの位置合わせ
- ・高速PDを使ったXFELと同期レーザーのタイミング調整
ビームタイム中にユーザーが行うこと
- ・持ち込み装置設置・アライメント
- ・試料の交換
- ・インジェクターの交換
- ・試料(インジェクター)の位置調整
- ・精密な時間原点の決定(TimeZeroFinder)
測定手順
アライメント
- ・溶液ジェットの中心にXFELが照射されるようインジェクターの位置を調整
- ・同期レーザーの条件を適切に設定(delay、励起強度)
- ・同期レーザーがOnとOffの場合の差分信号を計測し、光励起に伴う過渡応答を検出
- ・同期レーザーの励起強度依存性を計測し、多光子過程が起こる閾値を決定。
- ・同期レーザーのdelay依存性を計測し、時間原点を精密に決定。
- ・ジェットが不安定になったり、詰まった場合はインジェクターの交換をし、インジェクターの位置を再調整。
ソフトウェア
時間分解X線分光(TR-XAS、TR-XES、TR-XSS)のデータ処理ソフトとして、OfflineAnalysis(python+Qt4)が利用可能です。詳細はこのメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。までお問い合わせください。
タイミングモニター
フェムト秒の時間分解能を得るためには、タイミングモニターを利用して計測終了後にデータを並べ替える必要があります。
参考文献:
T. Katayama et al., Struct. Dyn. 3, 034301 (2016).
K. Nakajima et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 25, 592 (2018).
X-Ray Spectrometry (Ultrafast Chemistry)
XFEL enables time-resolved X-ray measurements which combine high time-resolution (fs), high spatial-resolution (sub—Å) and element selectivity. These properties have led to rapid development of ultrafast X-ray science in recent years. SACLA shares SPINETT (SACLA Pump-probe INstrumEnt for Tracking Transient dynamics), which is available for measuring time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy (TR-XAS), time-resolved X-ray emission spectroscopy (TR-XES), and time-resolved X-ray solution scattering (TR-XSS) with femtosecond time-resolution. This page will introduce the SPINETT configuration, experimental procedures, and typical results.
References:
T. Katayama et al., Struct. Dyn. 6, 054302 (2019).
Basic Performance and Results
Observation of nuclear wave packet oscillation
Nuclear wave packets of Cu(I) bipyridine complexes
References:
T. Katayama et al., Nat. Commun. 10, 3606 (2019).
Visualization of chemical bond formation
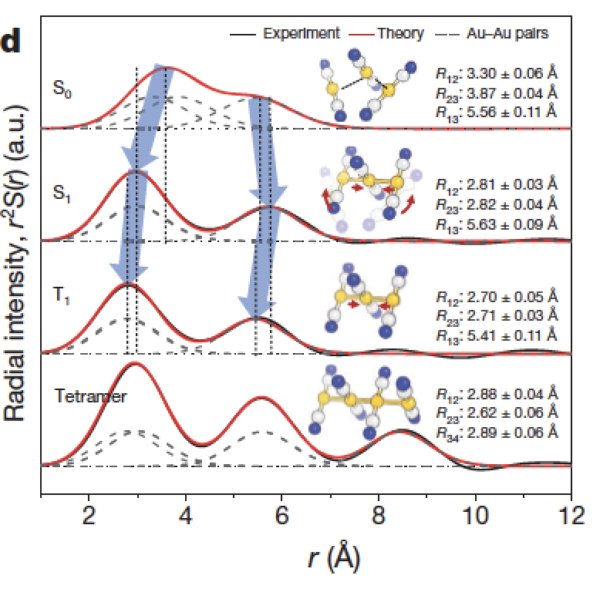
To track the formation process of 2 complex Au (CN) bonds
References:
K. H. Kim et al., Nature 518, 385 (2015).
Carrier dynamics of metal oxides
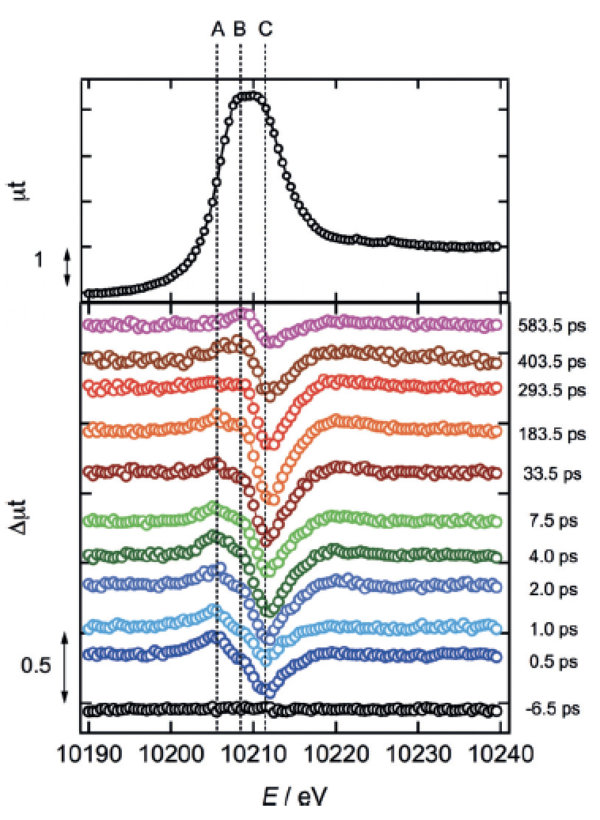
Time-resolved X-ray absorption spectrum of the WO3 L-III edge
References:
Y. Uemura et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 1364 (2016).
Experimental Equipment
SPINETT consists of a sample chamber, a Von Hamos spectrometer, and an MPCCD detector.
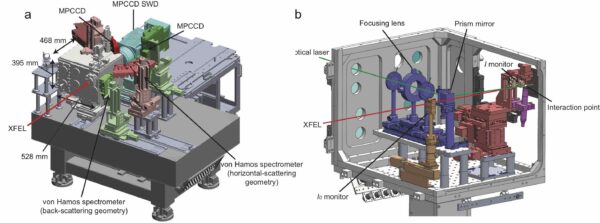
SPINETT gener
Sample chamber
In many cases, the sample is dissolved (dispersed) in a solvent, then discharged as a solution from the injector in the form of a jet. The diameter of the injector can be selected from 30 to 500 μm (the mismatch of group velocity dispersion caused by differences in the refractive index in synchronous lasers and the XFEL medium effects the time resolution of the measurement, so it must be selected according to the physical phenomenon you want to track). Inside the chamber, two X-ray intensity monitors are provided to measure the incident X-ray intensity and X-ray fluorescence intensity from the sample during TR-XAS experiments.
Von Hamos spectrometer
SPINETT is equipped with two energy dispersed spectrometers for TR-XES experiments. Both of the spectrometers can mount six 100 mm × 25 mm curved analyzer crystals (radius of curvature 250 mm). Currently available analyzer crystals include Si(531), Si(111), Ge(111) and Ge(220). When bringing in your own analyzer crystals, a meeting with the facility staff is required, as it is necessary to avoid interfering with the standard equipment. Please contact the XFEL Utilization Division (このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。 ) in advance.
<p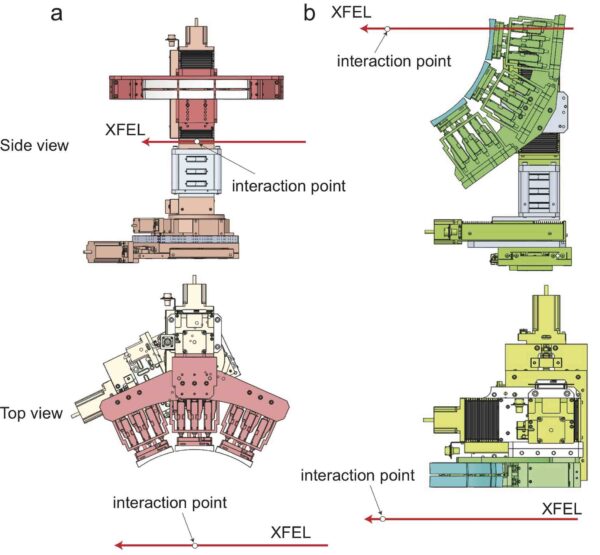 Von Hamos spectrometer
Von Hamos spectrometer
MPCCD detector
Two single MPCCD detectors for the Von Hamos spectroscope are available, and an SWD Octal MPCCD detector that can cover a wide-angle area for the TR-XSS measurements is located outside of the sample chamber. The minimum camera length for the SWD Octal MPCCD detector is ~55 mm. The minimum camera length can cover the reverse lattice space of 3.88Å-1 at 10keV and 5.82Å-1at 15keV.
Operating Parameters (EH2@BL3)
Time-resolved X-ray spectrometry experiments are mainly conducted at BL3EH2.
XFEL parameters
| Photon Energy (fundamental wave) | 4-20 keV |
| Pulse Energy | Photon energy (see figure below) |
| Energy Width (ΔE/E) | ~0.5%(without a two crystal spectrometer) |
| Repetition Rate | 30 Hz(BL2&3 simultaneous operation) |
References:
M. Yabashi et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 22, 477 (2015).
K. Tono et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 595 (2019).
(Reference) The relationship between the photon energy and the pulse energy/photon number (for BL3)
X-ray focusing special characteristics
| Optical parameters (CRLs) | |
| Material | Beryllium |
| Shape of lenses | Paraboloid |
| Radii of curvatures (R) | 200, 500 µm |
| Maximum number of lenses | 31 with R = 200 µm 15 with R = 500 µm |
| Focal length | 2.5 m |
| Spatial acceptance | > 0.9 mm |
| Divergent angle | > 0.1 mrad* |
| Typical focal size @10 keV | 1-2 µm FWHM* |
*Depending on the wavelength and number of lenses used
References:
T. Katayama et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 333 (2019).
Optical laser characteristics
| Fundamental Wave | 2nd Order Harmonic | 3rd Order Harmonic | 4th Order Harmonic | |
| Wavelength | 800 nm | 400 nm | 267 nm | 200 nm |
| Pulse Energy (Max.) | ~12 mJ | ~0.5 mJ | ~0.2 mJ | ~0.02 mJ |
| Pulse Duration | ~40 fs | ~30 fs | ~50 fs | |
| Rep. Rate | 60 Hz | 60 Hz | 60 Hz | 60 Hz |
In addition to the above, light from the optical parametric amplifier (OPA) is available. The available wavelength range is 0.25-2.6 µm, and the pulse energy depends on the wavelength as shown below.
Adjustments before the Measurement
What staff do before and during beam time
- ・Bring equipment into the experimental hutch
- ・XFEL spectral measurements, optical axis adjustments, focusing adjustments
- ・Monochromator alignments
References:
T. Katayama et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 26, 333 (2019).
- ・Von Hamos spectrometer alignment
- ・4 quadrant slit alignments
- ・MPCCD detector alignment
- ・Synchronous laser spectrum, optical axis and focusing alignments
- ・XFEL and synchronous laser matching
- ・Timing adjustments of XFEL and the synchronous laser using high-speed PD
What the user does during beam time
- ・Install and align all user provided equipment
- ・Sample exchange
- ・Injector exchange
- ・Sample (injector) location adjustment
- ・Precise origin time decisions (TimeZeroFinder)
Measurement Procedure
Alignment
- ・Adjust the position of the injector so that the XFEL is irradiated at the center of the solution jet
- ・Properly set the conditions of the synchronous laser (delay, excitation intensity)
- ・Measure the difference signal when the synchronous laser is on and off, then detect the transient response associated with photoexcitation
- ・Measure the excitation intensity dependence of the synchronous laser to determine the threshold at which the multiphoton process occurs
- ・Measure the delay dependence of the synchronous laser to precisely determine the time origin
- ・If the jet becomes unstable or clogged, replace the injector and readjust the position of the injector
Software
OfflineAnalysis (python + Qt4) is available as data processing software for time-resolved X-ray spectrometry (TR-XAS, TR-XES, TR-XSS). Please contact the このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。 for more details.
Timing Monitor
To obtain the time resolution in femtoseconds, the data must be sorted after the measurement is completed by using the timing monitor.
References:
T. Katayama et al., Struct. Dyn. 3, 034301 (2016).
K. Nakajima et al., J. Synchrotron Rad. 25, 592 (2018).
