放射光とは
| 放射光施設とは | 利用分野と研究例 | 歴史 | SPring-8とSACLA |

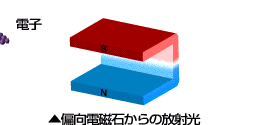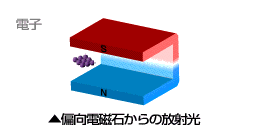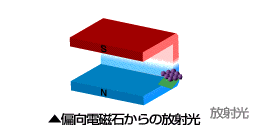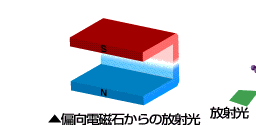
ほぼ光速で直進する電子が、その進行方向を磁石などによって変えられた際に発生する電磁波を放射光と呼びます。この現象は今から約50年前に電子シンクロトロン(電子加速器)で初めて観測されました。 放射光は、電子のエネルギーが高いほど指向性の高い明るい光となります。電子のエネルギーが高く、進む方向の変化が大きいほど、X線などの短い波長の光を含むようになります。
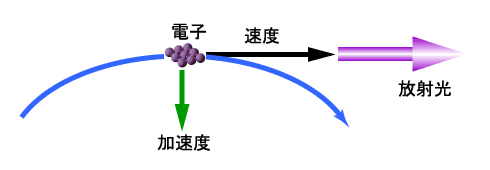
電子は負の電荷をもっているためその周りに電場をつくっており、仮想の光子を雲のようにまとっていると考えることができます。高エネルギーの電子が磁場で曲げられると仮想の光子が振り落とされて現実の光子となって放出されます。これが放射光です。
 |
 |
放射光施設とは
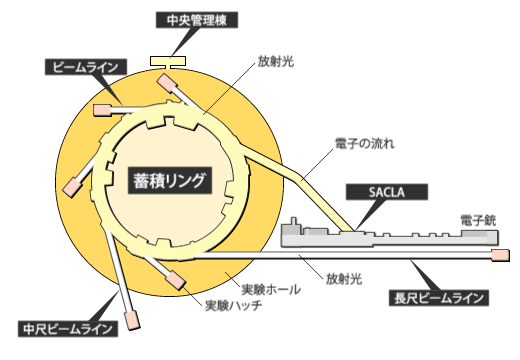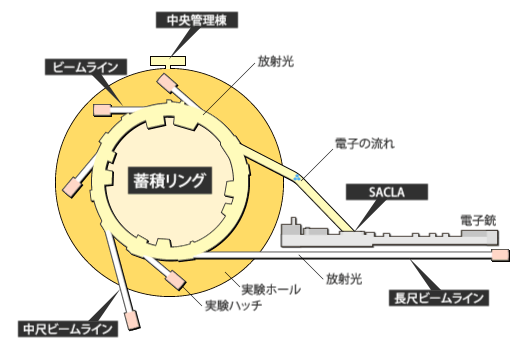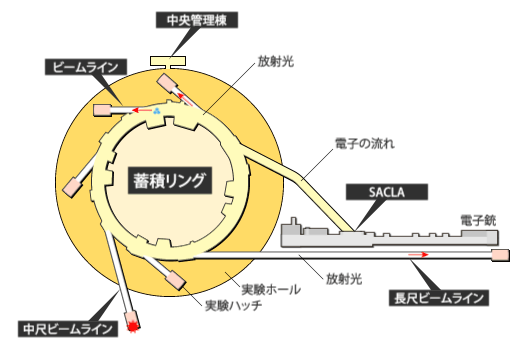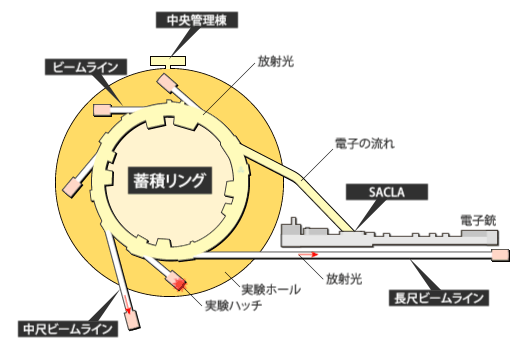
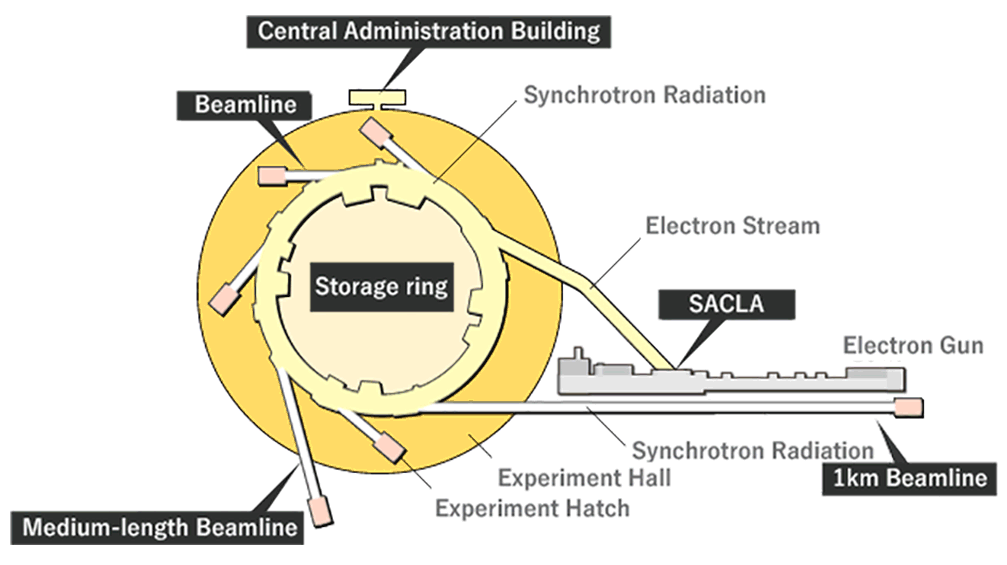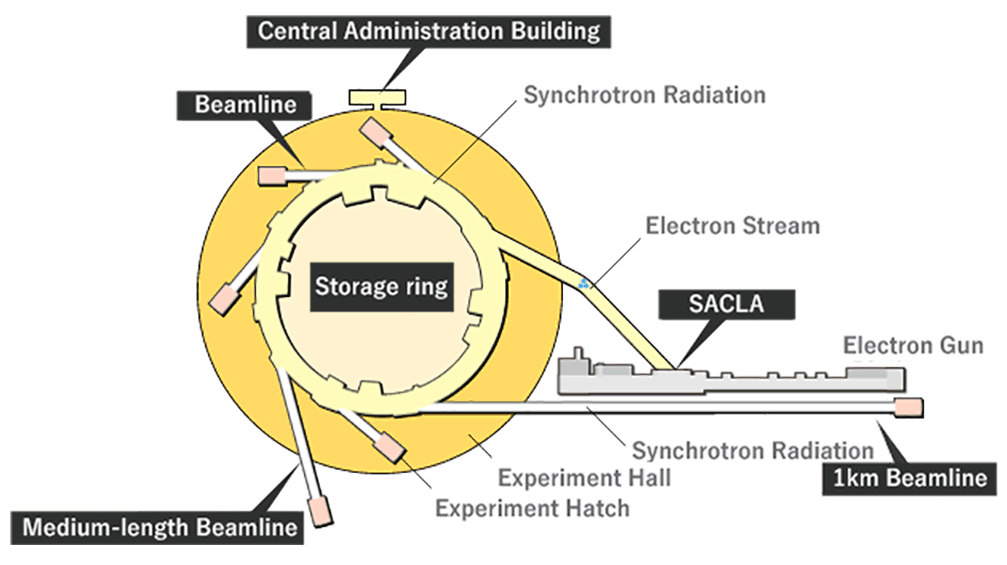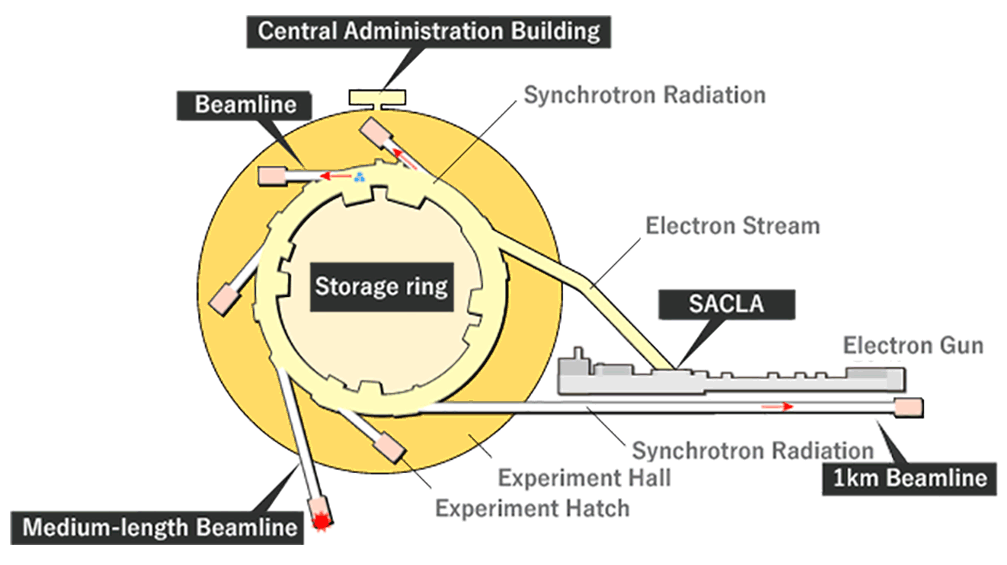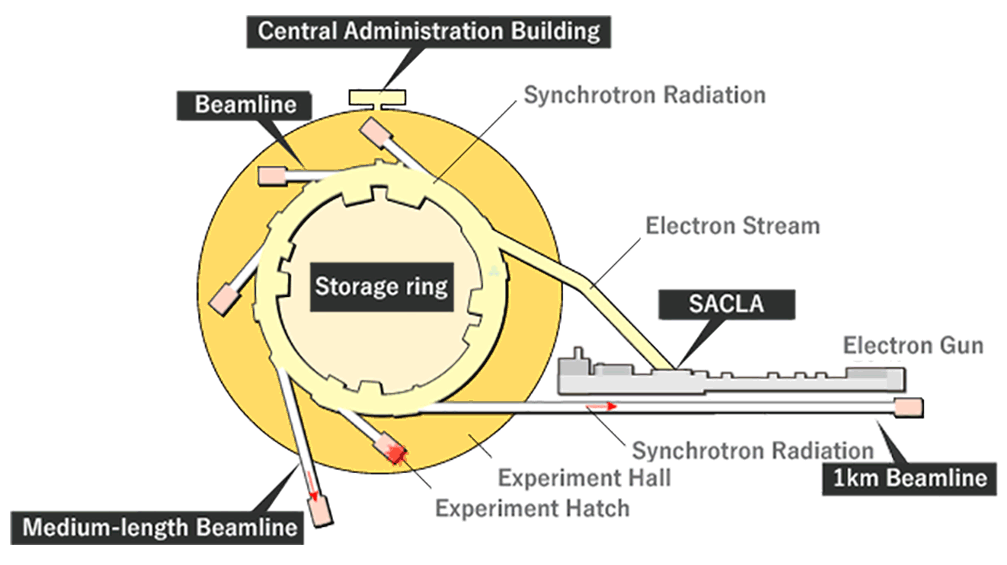
放射光施設とは、加速された高エネルギーの電子ビームから発生する放射光を利用して実験・研究する施設です。
利用分野と研究例
| 物質科学: | 先端材料の原子・電子の構造解析や極端条件下での材料物性や新物質創製や材料改質 |
| 生命科学/医学: | タンパク質などの生命物質の立体構造解析、例えば、生命のメカニズムの研究や医薬品開発、屈折コントラスト映像法による生体試料の高解像度イメージング |
| 環境科学: | 環境浄化用触媒の分析や生体試料中の環境汚染微量元素の分析 |
| 地球科学/宇宙科学: | 地球科学/宇宙科学:地球深部物質の構造と状態解析や隕石・宇宙塵の構造解析 |
| 産業利用: | 産業界における材料評価やタンパク質の立体構造解析 |
世界・日本の放射光施設と歴史
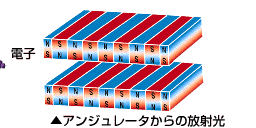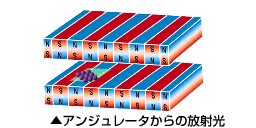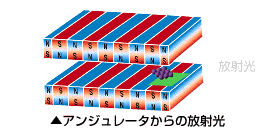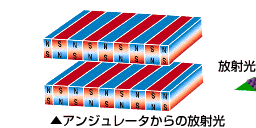
現在、世界には30を超える放射光施設が稼働中です。また、国内でも現在8施設が稼働中です。放射光施設の歴史は、第1世代として1940年代にシンクロトロンの誕生で放射光が初めて直接観察され、放射光の研究や利用が始まりました。次いで、第2世代として1970年代には加速器開発が進み、電子エネルギーが増大して、より波長の短いX線領域の放射光が得られるようになり、周回電子エネルギーを一定に保つ蓄積リングを利用して安定した放射光の供給化可能になりました。それにより放射光専用の加速器や実験設備が次々建設されました。1980年代以降のバイオテクノロジーやナノテクノロジーの発展で放射光の利用は急速に広まり、より高度化、多様化ニーズが増大し1990年代以降、より輝度の高い放射光を得るために高性能な蓄積リングとアンジュレータを組合せた第3世代放射光施設の建設が世界各国で始まりました。SPring-8もこの流れの中で誕生しました。
SPring-8とSACLA

SPring-8は世界の放射光科学をけん引する数々の新しいテクノロジーを開発してきました。それらを総合して作り上げたのが、全く新しいX線自由電子レーザー施設SACLAです。世界中に多数の放射光施設が建設されていますが、それらはSPring-8で作られた技術が使われています。ナノの世界を照らすSPring-8/SACLAは、単なる観察のための照明を超えて、ナノの世界が創りだす新機能の原因を解き明かす「ソリューション」を与えています。
What is Synchrotron Radiation (SR)?

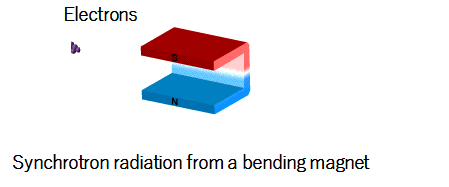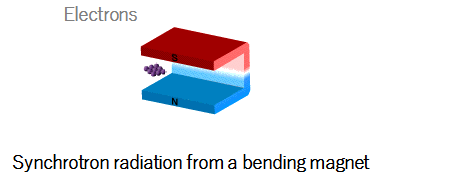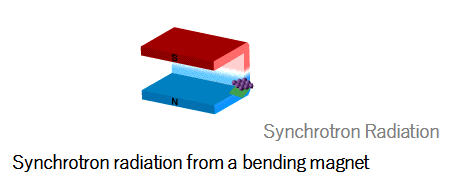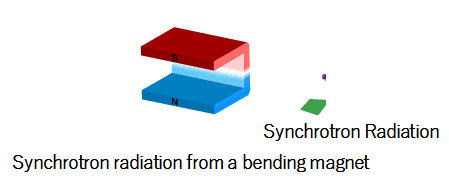
Electrons travelling in a straight line at approximately the speed of light generate electromagnetic waves when their moving direction is changed by the magnetic fields. The generated electromagnetic waves are known as Synchrotron Radiation, first observed about 50 years ago with an electron synchrotron (Electron accelerator). The brightness of the synchrotron radiation depends on the electron energy. Higher energy electrons with larger changes in direction results in shorter wavelengths of radiation, such as X-rays.
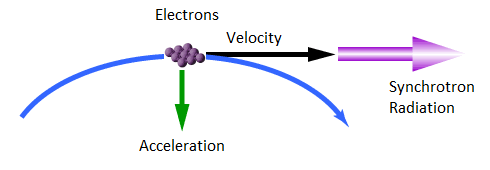
Electrons has negative charges that create a surrounding electric field, which is nothing but a virtual photon cloud. When a trajectory of high-energy electrons are bent by a magnetic field, the surrounding virtual photons are shaken off from the trajectory and emitted as real photons. This is the mechanism of the synchrotron radiation.
 |
 |
What is a Synchrotron Radiation Facility ?
A synchrotron radiation facility conducts research and experiments using synchrotron radiation generated from accelerated high-energy electron beams.
Fields of Use and Research Examples
| Material science: | Analysis of atomic and electronic structures, investigation of material properties under extreme conditions, and creation of new advanced/functional materials. |
| Life science / Medicine: | Three-dimensional structural analysis of life materials including proteins toward elucidation of the life mechanisms and drug development, and high-resolution imaging of biological samples by refractive contrast imaging. |
| Environmental science: | Analysis of catalysts for environmental purification, and analysis of contaminated trace elements in biological samples. |
| Earth Science / Astronomy: | Analysis of states and structures of deep earth materials, and structural analysis of meteorites and cosmic dust. |
| Industrial use: | Evaluation of industrial materials and three-dimensional structure analysis of proteins. |
The History of Synchrotron Radiation Facilities in Japan and the World
Currently, more than 30 synchrotron radiation facilities are in operation around the world, including 8 facilities in Japan. The history of synchrotron radiation facilities began in the 1940s when synchrotron radiation was first directly observed, which is regarded as the born of the first generation of synchrotrons. In the 1970s the second generation of accelerator development began; higher energy electrons were achievable, leading to the synchrotron radiation in shorter wavelengths even X-ray regions. Also the use of a storage ring made it possible to supply stable synchrotron radiation and keep the orbital electron energy. The success of the stable radiation triggered further development and construction of synchrotron radiation accelerators and experimental equipment. The importance of the synchrotron radiation spread rapidly with the development of biotechnology and nanotechnology in the 1980s. To meet more sophisticated and diverse needs grown up since the 1990s, the construction of third-generation synchrotron radiation facilities began in rush around the world, aiming to combine high-performance storage rings and undulators for brighter synchrotron radiation. In such situation, SPring-8 was constructed to become a flagship of the 3rd synchrotron facilities..
SPring-8 and SACLA

SPring-8 developed a number of new technologies that has made significant contribution to synchrotron radiation science around the world. These technologies realized SACLA, an X-ray Free Electron Laser Facility. SPring-8/SACLA has the ability to illuminates the nano world and also provides "solutions" to unravel the nano world.