- 詳細
- 投稿者: Super User
- カテゴリ: 設備
- 参照数: 676
多目的多軸X線回折計(2)
◆装置概要
BL46XUの第一実験ハッチ上流側に設置されています。汎用的に用いられる多軸X線回折計であり、無機・有機薄膜、金属、セラミック、複合材料等のX線回折を用いた評価が実施されています。主に産業界、産学連携ユーザーに利用されています。
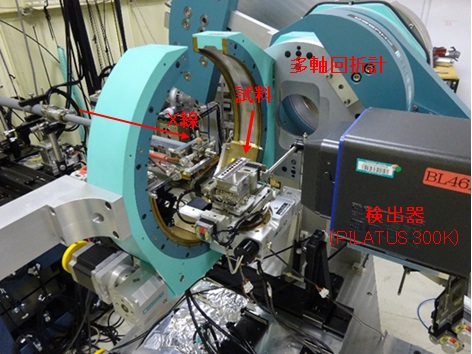
◆装置の特徴
回折計本回折計はHUBER社製の6軸回折計であり、試料周りの4軸(φ、χ、ω、ωz)、検出器軸の3軸(2θ、2θz、2θ2)から構成されています。アタッチメントとして試料周辺のxs、ys、zs、rxs、rys軸や、検出器軸のアナライザー結晶を取付けるためのtha、ttha軸を設置することもできます。
各軸の動き【リンク1】
検出器
実験の目的に応じて下記の検出器から選択することができます。0次元検出器と2次元検出器PILATUS 300Kの両方を検出器軸に設置することもできます。
・0次元検出器:NaIシンチレーション検出器(応用光研)
LaBr3シンチレーション検出器(FMB oxford)
・1次元検出器:6連装MYTHEN(dectris)
・2次元検出器:PILATUS 100K、300K、2M(dectris)
検出器の詳細な情報は下段の装置アクセサリーに項目に記載しています。
制御ソフトウェア
ビームライン・回折計の制御にはSPEC(Certified Scientific Software社)を用いています。
X線エネルギー
SPring-8標準アンジュレータ―と標準2結晶分光器(Si(111)面)を使用しています。使用できるX線エネルギーは1次光で4.5~37.5 keVの範囲です。
より高エネルギーのX線を使用する場合は3次光を用いることで60~80 keVを使用することもあります(この場合、1次光・4次光が混在します)。
ビームサイズ
ビームサイズは測定目的に応じて変化させます。
最大ビームサイズは横1.0㎜×縦0.7㎜程度
スリット成形による最小ビームサイズ:30 um×30 um程度
フレネルゾーンプレートによる最小ビームサイズ:3 um×10 um程度
ビーム強度
12.4 keV、ビームサイズ縦30 um×横400 um(スリット成形)の条件で
約5.0 × 1011 photons/sec
その他
・本多軸回折計とほぼ同じ仕様の多軸回折計がBL19B2の第2ハッチに設置されており、装置アクセサリーや制御環境の共通化を図っています。実験の目的に応じて挿入光源(BL46XU)と偏向電磁石光源(BL19B2)を選択することができます。
・本多軸回折計の下流側にフリースペース【リンク2】があります。大きさは2.0 m(光軸方向)×2.5 m(光軸直交方向)×2.0 m(高さ)です。ユーザー持込装置を用いた実験や、多軸回折計を用いない回折実験、多軸回折計と組み合わせた実験等を実施することができます。
◆装置アクセサリー
試料位置合わせ用自動ステージ(多軸回折計phi軸に取り付け)
zs軸、xs軸、ys軸、rxs軸、rys軸
多軸回折計phi軸にzs軸を取付け、このzs軸上に実験に応じて各種自動ステージを設置します。詳細情報はこちら【リンク3】。
試料環境
・試料加熱装置【リンク4】(反射配置):アントンパール社DHS1100(室温から1100℃)
・試料冷却加熱装置【リンク5】(反射配置):アントンパール社DCS500(-180℃から500℃)
・引張り試験機【リンク6】:最大引張り荷重2KN、試料サイズ長さ約3cm×幅約1cm×厚み約0.5㎜
検出器
・0次元検出器:NaIシンチレーション検出器(応用光研) 【リンク7】
LaBr3シンチレーション検出器(FMB oxford)【リンク8】
・1次元検出器:6連装MYTHEN(dectris) 【リンク9】
・2次元検出器:PILATUS 100K (dectris)
PILATUS 300K (dectris) 【リンク10】
PILATUS 2M (dectris)【リンク11】
検出器軸光学系(0次元検出器使用時)
・ダブルスリット【リンク12】
・ソーラースリット
・アナライザー結晶【リンク13】
集光素子
・ゾーンプレート
・屈折レンズ
◆実験・試料準備
本装置は多目的・多用途に利用されるX線回折計のため、試料・実験準備はそれぞれの実験毎に異なります。課題が採択されればビームライン担当者からご連絡させていただきます。
◆実験手順・注意事項
本装置は多目的・多用途に利用されるX線回折計のため、実験手順・注意事項はユーザー実験毎に異なります。そのため共通のマニュアル等は準備しておりませんが、ユーザー実験毎にユーザーさんとビームライン担当者が協力して実験手順書を作成することが多いです。
◆問い合わせ先
小金澤 智之(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
佐藤 真直(msato@ spring8.or.jp)
◆代表的な論文リスト
"Efficient inverted polymer solar cells employing favourable molecular orientation"
V. Vohra, et al.
Nature Photonics, 9, (2015) 403-408
https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2015.84
"Crystallization Dynamics of Organolead Halide Perovskite by Real-Time X-ray Diffraction"
T. Miyadera, et al.
Nano Lett., 15, (2015) 5630-5634
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02402
"Fe-Ni composition dependence of magnetic anisotropy in artificially fabricated L1 0-ordered FeNi films"
T. Kojima, et al.
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 26, (2014) 064207_1-10
https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/26/6/064207
"Ionic Conductivity in Ionic Liquid Nano Thin Films"
S. Maruyama, et al.
ACS Nano, 12, (2018) 10509-10517
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b06386
"Elastic and Plastic Deformation Behavior Studied by In-Situ Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction in Nanocrystalline Nickel"
H. Adachi, et al.
Materials Transactions, 57, (2016) 1447-1453
https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.MH201505
Multipurpose Multi-axis X-ray Diffractometer (2)
◆Equipment overview
This equipment is installed in the first experimental hatch in the upper course of BL46XU. It is a general-purpose, multi-axis X-ray diffractometer, which uses X-ray diffraction to evaluate inorganic and organic film, metals, ceramics, composite materials and more. It is mainly used for industrial and industrial-academic collaboration users.
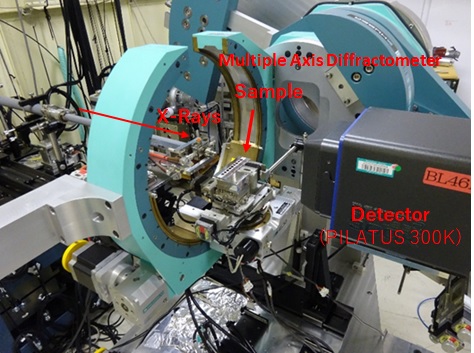
◆Features of the Equipment
DiffractometerThis diffractometer is a 6-axis diffractometer manufactured by HUBER, which consists of 4 axes around the sample(φ,χ,ω,ωz) and 3 detector axes(2θ,2θz, 2θ2). As well, xs,ys,zs,rxs,rys axes can be attached around the sample and tha,ttha axes for mounting analyzer crystals can be installed on the detector axis.
Movement of each axis【Link 1】
Detector
Depending on the purpose of the experiment, any of the following detectors can be chosen. Both the 0-dimensional detector and the 2-dimensional detector PILATUS 300K can be installed on the detector axis.
・0-Dimensional Detector: NaI scintillation detector (Photon application)
LaBr3 scintillation detector (FMB oxford)
・1-Dimensional Detector: 6-Fold MYTHEN(dectris)
・2-Dimensional Detector: PILATUS 100K, 300K, 2M (dectris)
Detailed information on the detector can be found in the equipment accessories section below.
Control Software
SPEC (Certified Scientific Software)is used to control the beamline and the diffractometer.
X-ray Energy
The standard SPring-8 undulator and standard 2 crystal spectrometer (Si (111) plane) is used. The available X-ray energy ranges from 4.5~37.5 keV for primary light.
As for high-energy X-rays, X-rays with 60-80 keV are available by using 3rd-order emitted light (mixed with 1st- and 4th-order light).
Beam Size
The beam size changes depending on the measurement objectives.
The maximum beam size is approximately 1.0 mm wide by 0.7 mm high.
The minimum beam slit size: approximately 30 um×30 um
The minimum beam size by Fresnel Zone Plate: Approximately 3 um×10 um
Beam Intensity
12.4 keV, with a beam size length of 30 um and width 400 um (slit configuration) of approximately 5.0 × 1011 photons/sec
Other
・A multi-axis diffractometer with almost the same specifications as this multi-axis diffractometer is installed in the second hatch of the BL19B2, which shares equipment accessories and control environments. Depending on the purpose of the experiment, you can select an inserted light source (BL46XU) and a bending electromagnet light source (BL19B2).
・There is a free space 【Link 2】 on the downstream side of the multi-axis diffractometer. The size is 2.0 m (in the optical axis direction) by 2.5 m (in the optical axis orthogonal direction) by 2.0 m (height). Experiments can be carried out using user provided equipment or diffraction experiments can be conducted without multi-axis instruments, and multi-axis diffractometers.
◆Equipment accessories
Automated stage for sample alignment (installed on the multi-axis diffractometer phi-axis)
zs-axis, xs-axis, ys-axis, rxs-axis, rys-axis
The zs-axis is mounted on the multi-axis diffractometer phi-axis, and various automated stages are installed on the zs axis according to the experiment. Click here for more details 【Link 3】.
Sample Environment
・Sample Heating Equipment【Link 4】(Reflection configuration): Anton Paar DHS1100 (Room Temperature to 1100℃)
・Sample Cooling and Heating Equipment 【Link 5】(Reflection configuration): Anton Paar DCS500 (-180℃ to 500℃)
・Tension Test Machine【Link 6】: Maximum tension load 2KN, same length 3cm x width 1cm x thickness 0.5 mm.
Detector
・0-Dimensional Detector: NaI scintillation detector (Photon application) 【Link 7】
LaBr3 scintillation detector (FMB oxford) 【Link 8】
・1-Dimensional Detector: 6-fold MYTHEN (dectris) 【Link 9】
・2-Dimenstional Detector: PILATUS 100K (dectris)
PILATUS 300K (dectris) 【Link 10】
PILATUS 2M (dectris) 【Link 11】
Detector axis optical systems (when using a 0-dimensional detector)
・Double slit 【Link 12】
・Solar Slit
・Analyzer Crystal 【Link 13】
Concentration Elements
・Zone Plate
・Refractive Lens
◆Experiment / sample preparation
This equipment is a versatile, multipurpose X-ray diffractometer with sample and experiment preparation different for each experiment. If the assignment is selected, the beamline representative will contact you.
◆Experimental procedure / precautions
This equipment is a versatile, multipurpose X-ray diffractometer, with experimental procedures and precautions different for each user experiment. Therefore, we do not prepare common manuals but for each user experiment, users and beamline personnel will often work together to create experimental procedures.
◆Contact
小金澤 智之(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
佐藤 真直(msato@ spring8.or.jp)
◆List of representative treatises
"Efficient inverted polymer solar cells employing favourable molecular orientation"
V. Vohra, et al.
Nature Photonics, 9, (2015) 403-408
https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2015.84
"Crystallization Dynamics of Organolead Halide Perovskite by Real-Time X-ray Diffraction"
T. Miyadera, et al.
Nano Lett., 15, (2015) 5630-5634
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02402
"Fe-Ni composition dependence of magnetic anisotropy in artificially fabricated L1 0-ordered FeNi films"
T. Kojima, et al.
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 26, (2014) 064207_1-10
https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/26/6/064207
"Ionic Conductivity in Ionic Liquid Nano Thin Films"
S. Maruyama, et al.
ACS Nano, 12, (2018) 10509-10517
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b06386
"Elastic and Plastic Deformation Behavior Studied by In-Situ Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction in Nanocrystalline Nickel"
H. Adachi, et al.
Materials Transactions, 57, (2016) 1447-1453
https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.MH201505
