汎用型多軸回折計
◆装置概要
冷凍機を用いた低温実験や外場下での歪み・応力測定などを行うことができます。材料の表面から内部までの非破壊測定手法などに利用されています。
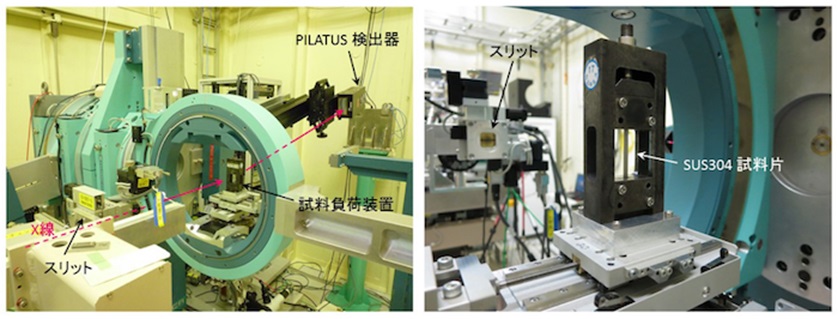
◆装置の特徴
回折計本回折計はHUBER社製の7軸回折計であり、試料周りの4軸(φ、χ、ω、ωz)、検出器軸の3軸(2θ、2θz、2θ2)から構成されています。アタッチメントとして試料周辺のxs、ys、zs軸や、検出器軸のアナライザー結晶を取付けるためのtha、ttha軸を設置することもできます。
検出器
実験の目的に応じて下記の検出器から選択することができます。0次元検出器と2次元検出器の両方を検出器軸に設置することもできます。
・0次元検出器:NaIシンチレーション検出器(応用光研)
・2次元検出器:PILATUS 1M CdTe(Dectris)、Mercury2 CCD(Rigaku)
制御ソフトウェア
ビームライン・回折計の制御にはSPEC(Certified Scientific Software社)を用いています。
X線エネルギー
SPring-8の偏向電磁石からの光源を標準2結晶分光器(Si(311)面)で分光して使用しています。使用できるX線エネルギーは8~115keVの範囲ですが、標準的には、18〜72keVの範囲での使用を推奨しています。
ビームサイズ
ビームサイズは測定目的に応じて変化させることができます。最小ビームサイズは横0.1㎜×縦0.1㎜程度です。
◆装置アクセサリー
試料位置合わせ用自動ステージ(多軸回折計phi軸に取り付け)
zs軸、xs軸、ys軸
試料環境
クライオスタット型温度可変装置(5〜)
検出器
・0次元検出器:NaIシンチレーション検出器(応用光研)
・2次元検出器:PILATUS3 1M CdTe (Dectris)
Mercyry2 CCD (Rigaku)
検出器軸光学系(0次元検出器使用時)
・ダブルスリット
・ソーラースリット
・アナライザー結晶
◆実験・試料準備
本装置は多目的・多用途に利用されるX線回折計のため、試料・実験準備はそれぞれの実験毎に異なります。課題が採択されればビームライン担当者からご連絡させていただきます。
◆実験手順・注意事項
本装置は多目的・多用途に利用されるX線回折計のため、実験手順・注意事項はユーザー実験毎に異なります。
そのため共通のマニュアル等は準備しておりませんが、ユーザー実験毎にユーザーとビームライン担当者が協力して実験手順書を作成することが多いです。
◆問い合わせ先
杉本邦久(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
安田伸広(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
中村唯我(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
◆代表的な論文リスト
"Presence of ε-martensite as an Intermediate Phase during the Strain-Induced Transformation of SUS304 Stainless Steel"
Hatano Masaharu et al.
Philosophical Magazine Letters, 96, (2016) 220-227
DOI : 10.1080/09500839.2016.1190876
"Direct Observation of Lattice Symmetry Breaking at the Hidden-Order Transition in URu2Si2"
Tonegawa Sho et al.
Nature Communications, 5, (2014) 4188
DOI : 10.1038/ncomms5188
"Direct Observation of Field-induced Variant Transformation in Fe3Pt Using Pulsed Magnetic Field X-ray Diffraction"
Ouyang Zhongwen et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 102, (2007) 113917
DOI : 10.1063/1.2822278
"Structural Relations between Two Ground States of NaV2O5 under High Pressure: A Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction Study"
Ohwada Kenji et al.
Physical Review B, 76, (2007) 094113
DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevB.76.094113
"Ferroelectricity from Iron Valence Ordering in the Charge-Frustrated System LuFe2O4"
Ikeda Naoshi et al.
Nature, 436, (2005) 1136-1138
DOI : 10.1038/nature04039
"Relaxor-like Behavior in λ-(BETS)2FeCl4 Studied by SR X-Ray Diffraction"
Komiyama Satoshi et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73, (2004) 2385-2388
DOI : 10.1143/JPSJ.73.2385
"Magnetic Structure of CoO Studied by Neutron and Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction"
Tomiyasu Keisuke et al.
Physical Review B, 70, (2004) 184411
DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevB.70.184411
"Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction Study of a Charge Stripe Order in 1/8-doped La1.875Ba0.125-xSrxCuO4"
Kimura Hiroyuki et al.
Physical Review B, 67, (2003) 140503(R)
DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevB.67.140503
General-Purpose Multi-Axis Diffractometer
◆Equipment overview
It is possible to perform low-temperature experiments using the freezer and obtain external field stress measurements and more. This is used for non-destructive measurements from the surface of the material to the internal structure.
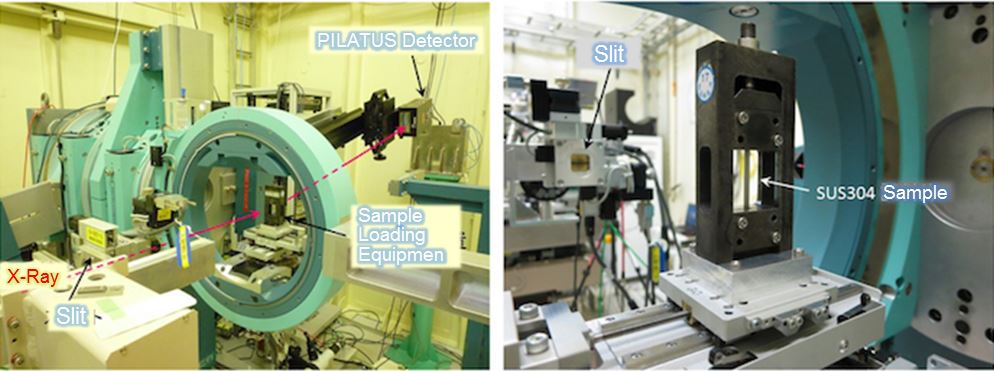
◆Features of the Equipment
DiffractometerThis diffractometer is manufactured by HUBER and is comprised of 7 axes, 4 axes(φ,χ,ω,ωz)around the sample, and 3 detector axes(2θ,2θz,2θ2). In addition, xs,ys,zs axes can be installed at the sample circumference, and tha,ttha axes can be installed at the crystal analyzer detector axis.
Detector
Depending on the purpose of the experiment, any of the following detectors can be chosen. Both 0-dimensional and 2-dimensional detectors can be installed on the detector axis.
・0-Dimensional Detector: NaI scintillation detector (Photon application)
・2-Dimensional Detector: PILATUS 1M CdTe(Dectris), Mercury2 CCD(Rigaku)
Control Software
SPEC (Certified Scientific Software) is used to control the beamline and diffractometer.
X-Ray Energy
The light source from the SPring-8 bending magnet is separated by a standard 2 crystal spectrometer(Si(311)face). The available X-ray energy range is 8~115keV, but it is recommended that a range of 18-72keV be used.
Beam Size
The beam size can be changed according to the measurement objective. The minimum beam size is 0.1mm x 0.1mm long.
◆Equipment accessories
Automated stage for sample positioning (Multi-axis diffractometer attached to the phi-axis)
zs-axis, xs-axis, ys-axis
Sample Environment
Cryostat temperature varying device (5〜)
Detector
・0-Dimensional Detector: NaI scintillation detector (Photon application)
・2-Dimensional Detector: PILATUS 1M CdTe(Dectris), Mercury2 CCD(Rigaku)
Detector axis optical systems (when using a 0-dimensional detector)
・Double Slit
・Solar Slit
・Analyzer Crystal
◆Experiment / sample preparation
This X-ray diffractometer has multi-purpose and versatile uses, where sample and experiment preparations are different for each experiment. If the assignment is selected, the person in charge of the beamline will contact you.
◆Experimental procedure / precautions
This X-ray diffractometer has multi-purpose and versatile uses, where sample and experiment preparations are different for each experiment.
Therefore, we do not prepare common manuals but for each user experiment, users and beamline personnel will often work together to create experimental procedures.
◆Contact
杉本邦久(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
安田伸広(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
中村唯我(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
◆List of representative treatises
"Presence of ε-martensite as an Intermediate Phase during the Strain-Induced Transformation of SUS304 Stainless Steel"
Hatano Masaharu et al.
Philosophical Magazine Letters, 96, (2016) 220-227
DOI : 10.1080/09500839.2016.1190876
"Direct Observation of Lattice Symmetry Breaking at the Hidden-Order Transition in URu2Si2"
Tonegawa Sho et al.
Nature Communications, 5, (2014) 4188
DOI : 10.1038/ncomms5188
"Direct Observation of Field-induced Variant Transformation in Fe3Pt Using Pulsed Magnetic Field X-ray Diffraction"
Ouyang Zhongwen et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 102, (2007) 113917
DOI : 10.1063/1.2822278
"Structural Relations between Two Ground States of NaV2O5 under High Pressure: A Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction Study"
Ohwada Kenji et al.
Physical Review B, 76, (2007) 094113
DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevB.76.094113
"Ferroelectricity from Iron Valence Ordering in the Charge-Frustrated System LuFe2O4"
Ikeda Naoshi et al.
Nature, 436, (2005) 1136-1138
DOI : 10.1038/nature04039
"Relaxor-like Behavior in λ-(BETS)2FeCl4 Studied by SR X-Ray Diffraction"
Komiyama Satoshi et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 73, (2004) 2385-2388
DOI : 10.1143/JPSJ.73.2385
"Magnetic Structure of CoO Studied by Neutron and Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction"
Tomiyasu Keisuke et al.
Physical Review B, 70, (2004) 184411
DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevB.70.184411
"Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction Study of a Charge Stripe Order in 1/8-doped La1.875Ba0.125-xSrxCuO4"
Kimura Hiroyuki et al.
Physical Review B, 67, (2003) 140503(R)
DOI : 10.1103/PhysRevB.67.140503
