時分割PDF解析装置
◆装置概要
大面積2次元検出器を利用し、広いQ範囲のデータを短時間で収集することができ、秒・分オーダーのPDF構造解析を行うことができます。マイクロウェーブ合成装置を用いた水熱合成環境下のPDF解析も可能です。
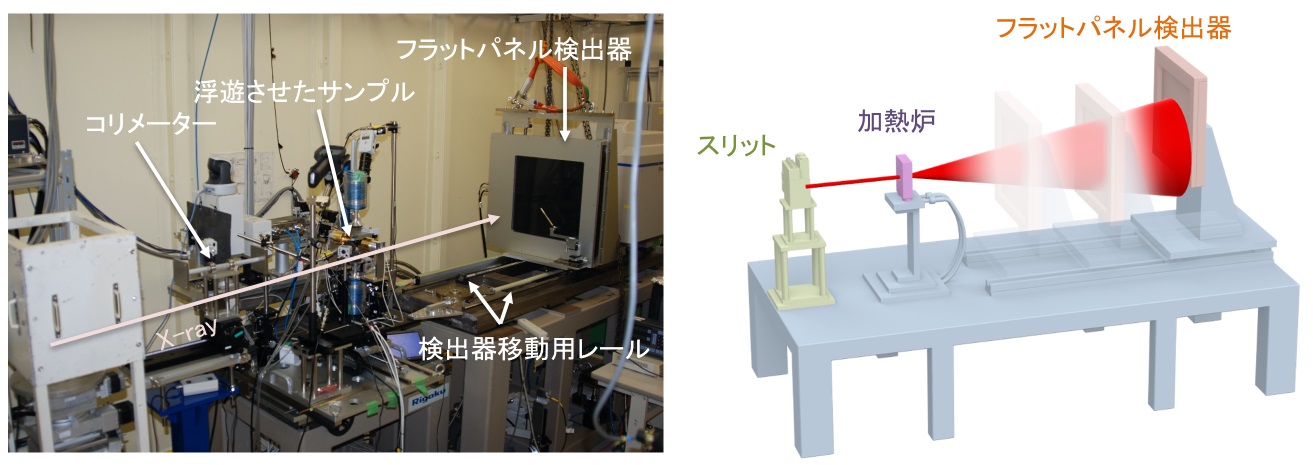
◆装置の特徴
カメラ長可変架台LMガイドを敷設した架台に検出器を設置しています。300 ~ 1,000 mmの範囲でカメラ長を変更し、目的に合わせたQ範囲、Q分解能のPDF解析データを取得することが可能です。(Qmax, dQ: 25, 0.02 Å-1 @カメラ長300 mm、Qmax, dQ: 12, 0.01 Å-1 @カメラ長800 mm、)
検出器
Varex社製フラットパネル検出器XRD1621 AN3が用意されています。
スペックは、下記の通りです。
材質 単層a-Si
検出面グレード CTグレード 不良1%以下
画素ピッチ 200µm
画素数 2048×2048ピクセル
検出エリア 409.6×409.6mm2
露光時間 66.6~999ms
シンチレータ CsI
寸法 672×599×44mm
重量 25kg
制御ソフトウェア
JASRIにて製作したGUI中心の制御となっています。
◆装置アクセサリー
高温電気炉(リガク製、室温〜1,100℃)
ガス浮遊炉(800〜3,000℃)
窒素吹きかけ式低温装置(オックスフォード製:Cryojet5、-196℃〜室温)
マイクロウェーブ合成装置(バイオタージ製、室温〜300℃、20bar)
◆実験・試料準備
試料容器としては、肉厚の薄いX線回折試料用キャピラリーがお勧めです。
(例えば、オーバーシーズ・エックスレイ・サービス製:http://www.oxs.co.jp)
内径2 ~ 3 mm程度のサイズのものがよく使われます。
また、室温実験の場合、バックグラウンドを抑えたポリイミドチューブ
(K-NEX製:http://www.kei-nex.com/process.html#pageLink01)も使われます。
試料をキャピラリーに充填し封止されて持ち込まれる場合、10-2Pa程度の真空度でリークチェックを事前にお願いします。
◆実験手順・注意事項
1.標準試料CeO2を試料マウント位置にセットし、X線を照射し2次元の回折像を取得します。
2.回折像を1次元化し、CeO2の既知結晶構造からカメラ長を算出します。
3.カメラ長を算出した後、測定したい試料をセットします。
4.ビームストップにカウンターが搭載されているため、サンプルの吸収によりサンプル位置を決めます。X方向(X線と直行する方向をXとしています)のスキャンを±2mmの範囲で行い、強度が最小となるXの値に調整します。
5.サンプルの位置出しが終了したら、本測定を開始します。本測定を開始する際には、検出器のオフセット測定(X線を照射せずにデータ取得しオフセット値として記憶させる測定)を、本測定と同じ条件で実施願います。
◆問い合わせ先
尾原 幸治(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
山田 大貴(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
◆代表的な論文リスト
"Geometrical Frustration of B-H Bonds in Layered Hydrogen Borides Accessible by Soft Chemistry"
Satoshi Tominaka, Ryota Ishibiki, Asahi Fujino, Kohsaku Kawakami, Koji Ohara, Takuya Masuda, Iwao Matsuda, Hideo Hosono, and Takahiro Kondo
Chem, 6, (2020) 406-418
DOI : 10.1016/j.chempr.2019.11.006
"Controlled Growth of SrxBa1−xNb2O6 Hopper‐ and Cube‐Shaped Nanostructures by Hydrothermal Synthesis"
Ola G. Grendal, Inger‐Emma Nylund, Anders B. Blichfeld, Satoshi Tominaka, Koji Ohara, Sverre M. Selbach, Tor Grande, and Mari‐Ann Einarsrud
Chemistry - A European Journal, 26, (2020) 9348-9355
DOI : 10.1002/chem.202000373
"In-situ Phase Identification of Crystallized Compound from 2CaO·SiO2–3CaO·P2O5 Liquid"
Masanori Suzuki, Sho Nakano, Honami Serizawa, and Norimasa Umesaki
ISIJ International, 60, (2020) 1127-1134
DOI : 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-449
"Observation of Liquid Phase Synthesis of Sulfide Solid Electrolytes Using Time‐Resolved Pair Distribution Function Analysis"
Koji Ohara, Naoya Masuda, Hiroshi Yamaguchi, Atsushi Yao, Satoshi Tominaka, Hiroki Yamada, Satoshi Hiroi, Masakuni Takahashi, Kentaro Yamamoto, Toru Wakihara, Yoshiharu Uchimoto, Futoshi Utsuno, and Shigeru Kimura
Physica Status Solidi B, (2020) Online publication 9 June 2020
DOI : 10.1002/pssb.202000106
"Structural Evolution of Amorphous Precursors toward Crystalline Zeolites Visualized by an in Situ X-ray Pair Distribution Function Approach"
Hiroki Yamada, Satoshi Tominaka, Koji Ohara, Zhendong Liu, Tatsuya Okubo, and Toru Wakihara
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 123, (2019) 28419-28426
DOI : 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b07232
Time-Resolved PDF Analysis Equipment
◆Equipment overview
Using a large area 2-dimensional detector, data in a wide Q range can be collected in second and minute orders for PDF structural analysis. Microwave synthesis equipment is also used to make PDF analysis possible in hydrothermal synthesis environments.
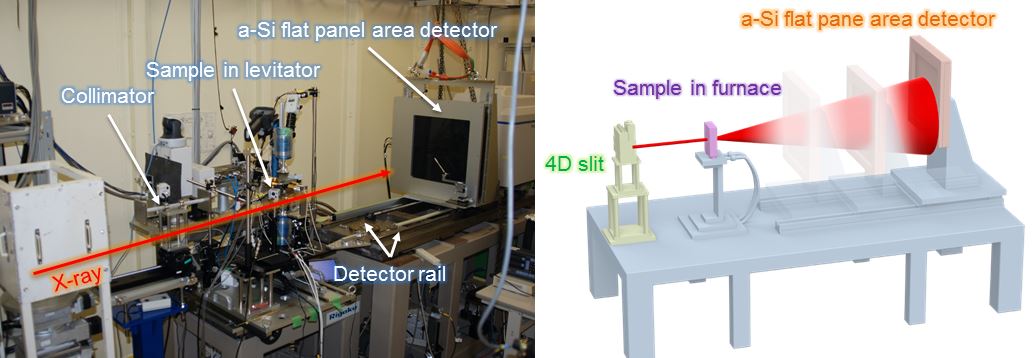
◆Features of the Equipment
Variable Length Mounted CameraA detector is installed at the LM Guide stand. It is possible to change the camera length from 300 – 1,000mm, to obtain PDF analysis with a wide Q range and Q resolution to suit the experiment objective. (Qmax, dQ: 25, 0.02 A-1 @Camera Length 300 mm、Qmax, dQ: 12, 0.01 A-1 @Camera Length 800 mm)
Detector
The Flat Panel Detector XRD1621 AN3 manufactured by Varex is available.
The specifications are as follows:
Material: Amorphous Si single layer
Detection Surface Grade: CT Grade, defect rate of less than 1%
Pixel Pitch: 200μm
Number of Pixels: 2048×2048 Pixels
Detection Area: 409.6×409.6mm2
Exposure Time: 66.6~999ms
Scintillator: CsI
Dimensions: 672×599×44mm
Weight: 25kg
Control Software
This software is controlled by a GUI and was created by JASRI.
◆Equipment accessories
High Temperature Electric Furnace (Manufactured by Rigaku: room temperature to 1,100℃)
Gas Suspension Furnace (800℃ to 3,000℃)
Low Temperature Nitrogen Spraying Device (Manufactured by Oxford: Cryojet 5, -196℃ to Room Temperature)
Microwave Synthesis Equipment (Manufactured by Biotage, from room temperature to 300℃, 20bar)
◆Experiment / sample preparation
For thin X-ray diffraction samples, a capillary is recommended for the sample container.
(One example is manufactured by Overseas X-Ray Service: http://www.oxs.co.jp )
Sizes with inner diameter between 2-3mm are often used.
Also, for room temperature experiments, a background suppressing polyimide tube is also used (manufactured by K-NEX: http://www.kei-nex.com/process.html#pageLink01).
After filling the capillary with the sample and sealing, in advance to bringing the sample to the experiment, please perform a vacuum leak test to an approximate degree of 10-2Pa.
◆Experimental procedure / precautions
1.Set the standard CeO2 sample at the sample mount location, X-ray irradiation is then used to obtain a two-dimensional diffraction image.
2.The one-dimensional diffraction image can be calculated by knowing the CeO2 crystal structure and the camera length.
3.After calculating the camera length, set the sample you wish to measure.
4.The beam stop is equipped with a counter, so the sample location is decided by absorbing the sample. Scan the X direction (The X direction is the direction the X-rays are travelling) within a ±2mm range, then adjust X to the value of minimal intensity.
5.When the sample is properly positioned, start this measurement. When beginning this measurement, please perform an offset measurement of the detector (a measurement that acquires data without X-rays irradiation and stores it as an offset value) under the same conditions as the measurement.
◆Contact
尾原 幸治(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
山田 大貴(このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。)
◆List of representative treatises
"Geometrical Frustration of B-H Bonds in Layered Hydrogen Borides Accessible by Soft Chemistry"
Satoshi Tominaka, Ryota Ishibiki, Asahi Fujino, Kohsaku Kawakami, Koji Ohara, Takuya Masuda, Iwao Matsuda, Hideo Hosono, and Takahiro Kondo
Chem, 6, (2020) 406-418
DOI : 10.1016/j.chempr.2019.11.006
"Controlled Growth of SrxBa1?xNb2O6 Hopper‐ and Cube‐Shaped Nanostructures by Hydrothermal Synthesis"
Ola G. Grendal, Inger‐Emma Nylund, Anders B. Blichfeld, Satoshi Tominaka, Koji Ohara, Sverre M. Selbach, Tor Grande, and Mari‐Ann Einarsrud
Chemistry - A European Journal, 26, (2020) 9348-9355
DOI : 10.1002/chem.202000373
"In-situ Phase Identification of Crystallized Compound from 2CaO・SiO2?3CaO・P2O5 Liquid"
Masanori Suzuki, Sho Nakano, Honami Serizawa, and Norimasa Umesaki
ISIJ International, 60, (2020) 1127-1134
DOI : 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-449
"Observation of Liquid Phase Synthesis of Sulfide Solid Electrolytes Using Time‐Resolved Pair Distribution Function Analysis"
Koji Ohara, Naoya Masuda, Hiroshi Yamaguchi, Atsushi Yao, Satoshi Tominaka, Hiroki Yamada, Satoshi Hiroi, Masakuni Takahashi, Kentaro Yamamoto, Toru Wakihara, Yoshiharu Uchimoto, Futoshi Utsuno, and Shigeru Kimura
Physica Status Solidi B, (2020) Online publication 9 June 2020
DOI : 10.1002/pssb.202000106
"Structural Evolution of Amorphous Precursors toward Crystalline Zeolites Visualized by an in Situ X-ray Pair Distribution Function Approach"
Hiroki Yamada, Satoshi Tominaka, Koji Ohara, Zhendong Liu, Tatsuya Okubo, and Toru Wakihara
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 123, (2019) 28419-28426
DOI : 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b07232
