エネルギー分散型XAFS (DXAFS)計測装置
◆装置概要
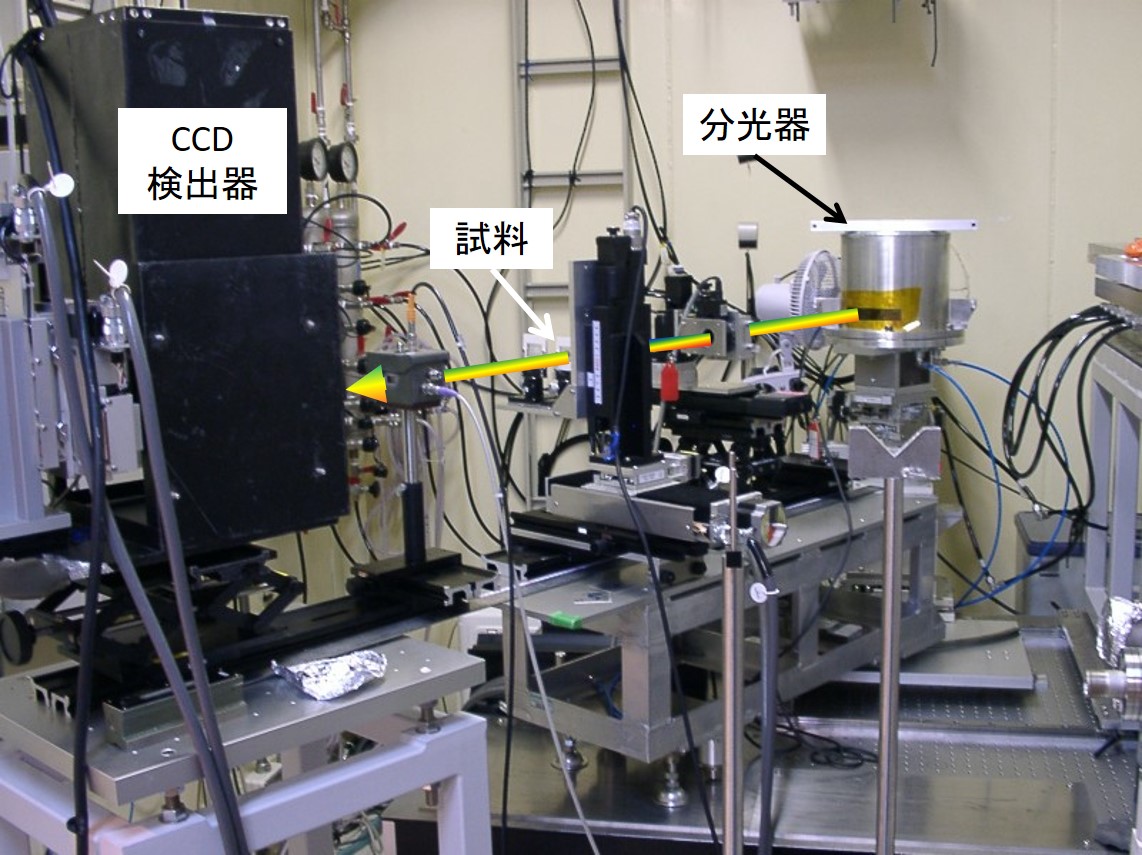
本システムは、湾曲した分光結晶と位置敏感型検出器によってXAFSスペクトルの全領域を一度に測定することができる装置です。ミリ秒オーダーの時間分解測定が可能です。
◆装置の特徴
本システムは、高調波除去ミラー、ポリクロメーター、可視光変換型2次元検出器から構成されています。ポリクロメーターはブラッグ型、ラウエ型の2種類あり、概ね7~12keVの低エネルギー領域はブラッグ型、12keVより高エネルギー領域ではラウエ型を使用します。試料位置での集光サイズは横方向で20-200μmです。可視光変換型2次元検出器
本システムの検出器として、可視光変換型2次元検出器が用意されています。蛍光体は、主に変換効率が高いP43(Gd2O2S:Tb3+)を、2次元検出器には浜松ホトニクス製 C4880-80または、より高速測定が可能な浜松ホトニクス製 Orca flashを用意しています。
制御ソフトウェア
装置の制御、XAFS計測は、NI社製のLabVIEWで作製されたプログラムを使用して行います。試料環境制御(温度、ガスバルブ開閉など)とXAFS計測が連動した測定が可能です。
◆装置アクセサリー
●透過法用in-situガス流通式加熱セル
温度範囲:室温 ~ 1073K
●バッチ式高速ガス置換システム
温度範囲:室温 ~ 973K
圧力:0.1Pa ~ 101.3kPa
圧力計応答性:<5msec
温度応答性:100ms
●マスフローコントローラー
He:300ml/min、H2:10ml/min,O2:50ml/min, CO:10ml/min,
NO:10ml/min
●ガス切替混合器
最大ガス数:4系統
●4重極型質量分析計(1~100amu)*BL01B1と共用
●ガス供給除害設備
可燃性:2系統
支燃性:2系統
使用(処理)可能ガス:He,H2,O2,HC,CO,NO, NH3
◆実験・試料準備
予め試料の組成をICP発光分析などで調べておくことをお勧めします。XAFS試料調製ガイドプログラム(産業利用推進室)などの計算ソフトを用いて測定に必要な量を求めて、調製された状態で持ち込まれることを推奨します。
◆実験手順・注意事項
①エネルギー較正を行うために、標準試料を測定します。
②in-situガス流通式加熱セルの設置やガス配管など試料回りの装置の組み立てを行います。
③試料をX線の集光点に設置するために、自動ステージを使用して試料の位置を調整します。
④検出器制御プログラムにより、検出器の露光時間を調整します。
⑤In-situ測定に適した計測プログラムを使ってin-situ測定を行います。
◆問い合わせ先
加藤和男 このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。
◆代表的な論文リスト
"Time Resolved in situ DXAFS Revealing Highly Active Species of PdO Nanoparticle Catalyst for CH4 Oxidation"
Mahara Yuji
ChemCatChem, 10, (2018) 3384-3387
DOI : 10.1002/cctc.201800573
"Striking Oxygen-Release/Storage Properties of Fe-Site-Substituted Sr3Fe2O7−δ"
Beppu Kousuke
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 122, (2018) 11186-11193
DOI : 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12754
"In situ X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study on Water Formation Reaction of Palladium Metal Nanoparticle Catalysts"
Matsumura Daiju
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42, (2017) 7749-7754
DOI : 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.08.189
"Hydrogen-Mediated Electron Doping of Gold Clusters As Revealed by In Situ X-ray and UV-vis Absorption Spectroscopy"
Ishida Ryo
The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 8, (2017) 2368-2372
DOI : 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b00722
"In Situ and Real-Time Monitoring of Oxide Growth in a Few Monolayers at Surfaces of Platinum Nanoparticles in Aqueous Media"
Imai Hideto
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 131, (2009) 6293-6300
DOI : 10.1021/ja810036h
Energy Dispersive XAFS (DXAFS) Measurement Equipment
◆Equipment overview
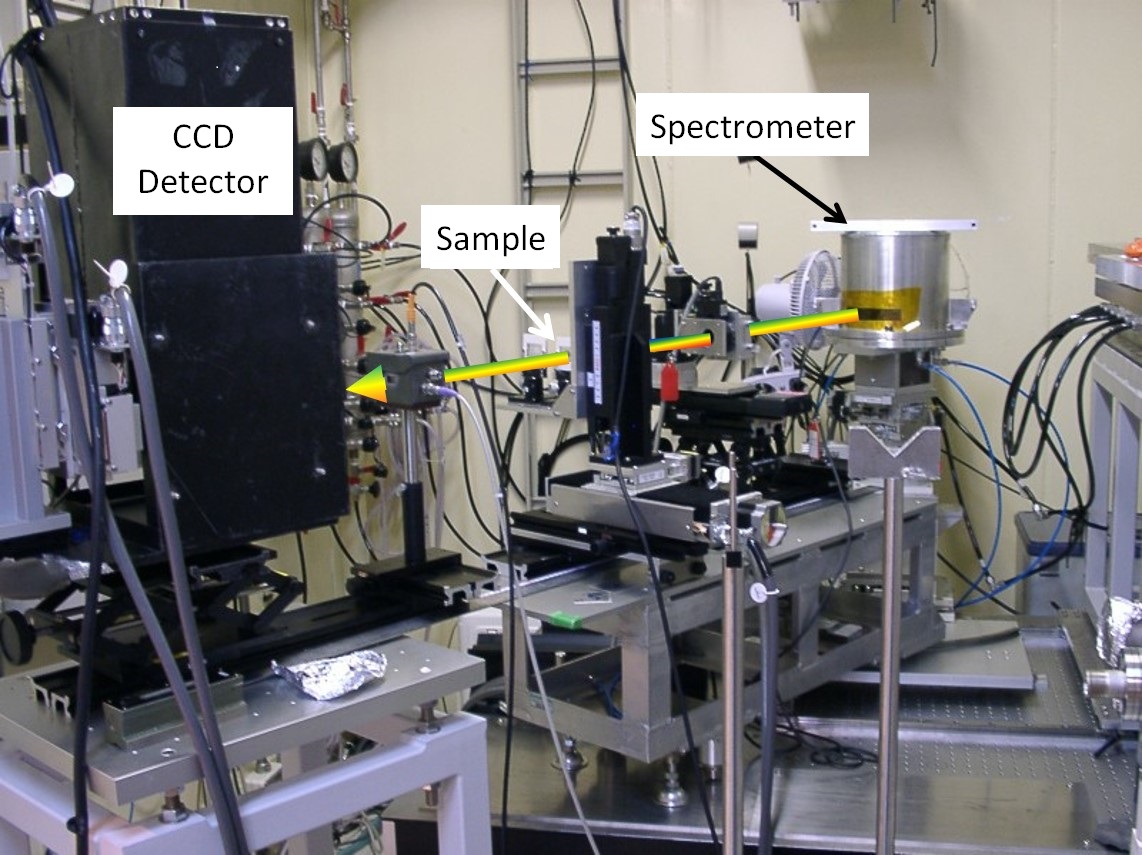
This system consists of equipment that can measure the entire range of the XAFS system at once, using curved analyser crystals and position sensitive detectors. Time-resolution measurements on the millisecond order are possible.
◆Features of the Equipment
This system is a visible light conversion 2-dimensional detector which is configured with a high-harmonic removal mirror and polychromators. There are two types of polychromators, a Bragg polychromator used for the low-energy region of roughly 7~12keV, and a Laue polychromator for high energy regions. The light collection size at the sample position is between 20-200μm laterally.Visible Light Conversion 2-Dimensional Detector
A visible light conversion 2-dimensional detector is available as a detector for this system. Fluorescent substances are mainly available with the high conversion efficiency P43(Gd2O2S:Tb3+), and the 2-dimensional detector C4880-80 manufactured by Hamamatsu Photonics, or the high-speed measurement range Orca Flash also manufactured by Hamamatsu Photonics.
Control Software
Equipment control and XAFS measurements are performed using a program made by LabVIEW, which is manufactured by NI. Sample environment control (temperature, opening and closing of the gas valves, etc) and XAFS measurements can be performed in tandem.
◆Equipment accessories
●Transmission in-situ gas flow heating cell
Temperature range: Room temperature ~ 1073K
●Batch high-speed gas replacement system
Temperature range: Room temperature ~ 973K
Pressure: 0.1Pa ~ 101.3kPa
Pressure gauge response: <5msec
Temperature response: 100ms
●Mass flow control
He:300ml/min、H2:10ml/min,O2:50ml/min, CO:10ml/min,
NO:10ml/min
●Gas mixing system
Maximum number of gasses: 4
●4 Heavy pole mass spectrometer (~100amu)* shared with BL01B1
●Gas supply and abatement equipment
Inflammability: 2 systems
Flammability:2 systems
Available gasses (processed): He,H2,O2,HC,CO,NO, NH3
◆Experiment / sample preparation
It is recommended that the composition of the sample be analysed by ICP emission analysis before being brought in. It is also recommended that you use calculation software such as XAFS Sample Preparation Guide Program (Industrial Use Promotion Office) or something similar to calculate the amounts required for measurements and sample preparations.
◆Experimental procedure / precautions
①Measure the standard samples to perform energy calibration.
②Assemble the in-situ gas flow heating cell and gas plumbing around the sample.
③Place the sample in the X-ray center by using the automated stage to adjust the position of the sample.
④Use the detector control program to adjust the detector exposure time.
⑤Complete in-situ measurements using a measurement program suitable for in-situ measurements.
◆Contact
加藤和男 このメールアドレスはスパムボットから保護されています。閲覧するにはJavaScriptを有効にする必要があります。
◆List of representative treatises
"Time Resolved in situ DXAFS Revealing Highly Active Species of PdO Nanoparticle Catalyst for CH4 Oxidation"
Mahara Yuji
ChemCatChem, 10, (2018) 3384-3387
DOI : 10.1002/cctc.201800573
"Striking Oxygen-Release/Storage Properties of Fe-Site-Substituted Sr3Fe2O7?δ"
Beppu Kousuke
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 122, (2018) 11186-11193
DOI : 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12754
"In situ X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy Study on Water Formation Reaction of Palladium Metal Nanoparticle Catalysts"
Matsumura Daiju
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 42, (2017) 7749-7754
DOI : 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.08.189
"Hydrogen-Mediated Electron Doping of Gold Clusters As Revealed by In Situ X-ray and UV-vis Absorption Spectroscopy"
Ishida Ryo
The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 8, (2017) 2368-2372
DOI : 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b00722
"In Situ and Real-Time Monitoring of Oxide Growth in a Few Monolayers at Surfaces of Platinum Nanoparticles in Aqueous Media"
Imai Hideto
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 131, (2009) 6293-6300
DOI : 10.1021/ja810036h
